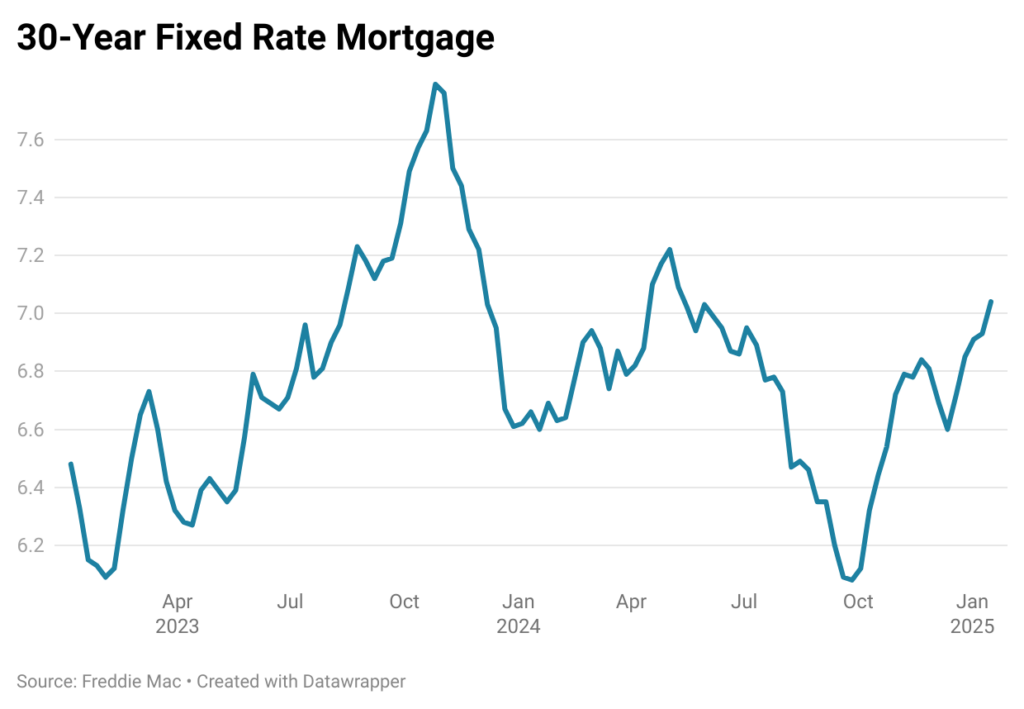
Housing was expected to become affordable in 2024, but mortgage rates remained elevated, and prices continued to increase. While a brief decline in mortgage rates to 6.08% in September offered a glimmer of hope, rates subsequently rebounded to 6.85% by year-end. This significant deviation from the widely predicted decline to the five percent range dashed hopes for improved affordability and significantly dampened buyer activity.
Home price appreciation, averaging 4.5% from October 2023 to October 2024 (FHFA), further exacerbated affordability concerns. However, this increase was not uniform since some markets remained flat and yet others posted price corrections. While the Northeast and Midwest witnessed substantial gains, some markets in Texas and Florida experienced price corrections.

Veros’ forecast anticipates that mortgage rates will stay elevated in the mid-six to seven percent range by 2025 end, but this is unlikely to significantly improve affordability. Mortgage rates closely track 10-year Treasury yields, which currently reflect expectations of persistent inflation and a limited number or no future Federal Reserve rate cuts. This suggests that borrowing costs will remain elevated, posing a continued challenge to homebuyers.
In addition to the challenges posed by elevated mortgage rates, the housing market is expected to experience continued price appreciation in 2025, with an average national increase of 2.7% (Q4 2024 VeroFORECASTSM). While regional variations will undoubtedly exist, with slower growth anticipated in the southern regions and stronger performance in the northeast, this continued price growth is a strong indicator of significant pent-up demand in the housing market.
Further challenging first-time home buyers is the prospect of rising property taxes and home insurance. Based on Insurify’s projections, the annual average home insurance across the U.S. is expected to have increased by 6% in 2024. States with the highest insurance costs such as Florida ($11,759), Louisiana ($7,809), and Oklahoma ($5,711) are prone to severe climate events such as hurricanes and tornadoes. These added costs could push the monthly mortgage payment beyond the reach of some homeowners’ budgets.
Property taxes have surged alongside rising property values. In 2023, the average property tax on single-family homes across the U.S. climbed 4.1% to $4,062, following a 3% increase the previous year, according to ATTOM Data. The Northeast emerged as the region with the highest property tax burdens, claiming seven of the top ten spots. New Jersey led the pack with an average property tax of $9,488, nearly ten times that of West Virginia, which boasted the lowest average levy at $989. Conversely, all ten states with the lowest average property taxes in 2023 were in the South.
Expect a continued challenging housing market in 2025. Elevated interest rates are expected to persist, while home prices continue their upward trajectory. The increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters will likely drive further increases in home insurance premiums. Coupled with persistently high property taxes, these factors create a significant hurdle for prospective homeowners. Prudent financial planning and diligent savings strategies will be crucial for many aspiring to achieve homeownership.

About Reena Agrawal, Research Economist
Reena Agrawal received her PhD in Economics from Vanderbilt University and MA in Economics from The Ohio State University and has several years of industrial experience in economic research and analysis.




